Hey guys,
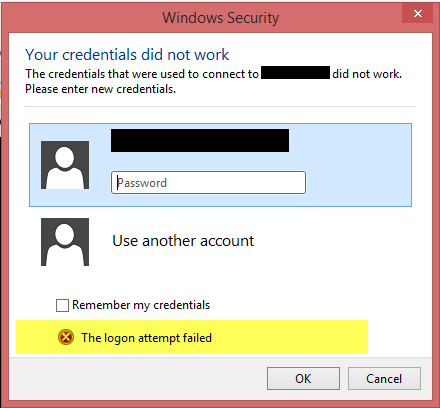
Everything has been working great until recently for some reason you cannot use your RDP client to access your remote server? Did your remote desktop client continues to pop-up and you’re sure that entered the right password? Or your session unexpectedly exits? The following procedure could work on you.
When attempting to start a remote desktop connection to a Win Server 2008 R2 machine, using a server local admin account on the remote machine, the error message provided was The logon attempt failed, this despite confirming the correct account details were used, account wasn’t locked out, etc.
In the security event log (eventvwr.msc) on the target machine, the following information was logged:
An account failed to log on.
Subject:
Security ID: NULL SID
Account Name: –
Account Domain: –
Logon ID: 0x0
Logon Type: 3
Account For Which Logon Failed:
Security ID: NULL SID
Account Name: AdminRMC
Account Domain: ******svr01
Failure Information:
Failure Reason: Unknown user name or bad password.
Status: 0xc000006d
Sub Status: 0xc000006a
Process Information:
Caller Process ID: 0x0
Caller Process Name: –
Network Information:
Workstation Name: ONE8-A12BCDEFG
Source Network Address: –
Source Port: –
Detailed Authentication Information:
Logon Process: NtLmSsp
Authentication Package: NTLM
Transited Services: –
Package Name (NTLM only): –
Key Length: 0
This event is generated when a logon request fails. It is generated on the computer where access was attempted.
The Subject fields indicate the account on the local system which requested the logon. This is most commonly a service such as the Server service, or a local process such as Winlogon.exe or Services.exe.
The Logon Type field indicates the kind of logon that was requested. The most common types are 2 (interactive) and 3 (network).
The Process Information fields indicate which account and process on the system requested the logon.
The Network Information fields indicate where a remote logon request originated. Workstation name is not always available and may be left blank in some cases.
The authentication information fields provide detailed information about this specific logon request.
– Transited services indicate which intermediate services have participated in this logon request.
– Package name indicates which sub-protocol was used among the NTLM protocols.
– Key length indicates the length of the generated session key. This will be 0 if no session key was requested.
Note: Error message available in the Security Event log, from Event Viewer, eventvwr.msc, or you can use PowerShell Get-WinEvent -Logname Security
The reason could be at the key LMCompatibility. He’s the responsible to control your NTLM authentication, it specifies the mode of authentication and session security to be used for network logons. Normally in a enterprise network this key is updated every time you reboot your laptop according to network policies.
LMCompatibility Levels:
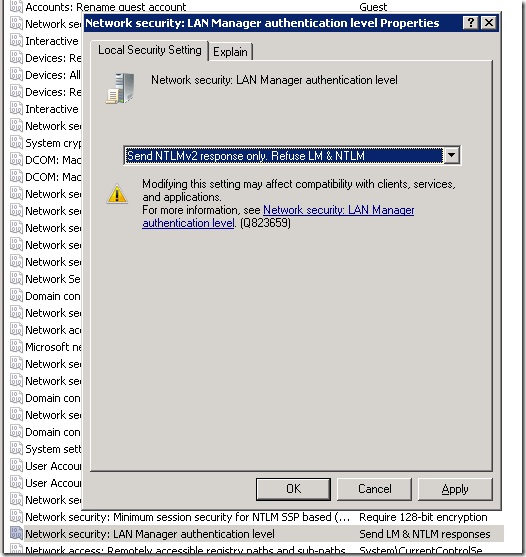
If you have access to the target server, go to “Run > SecPol.msc”. You should confirm the current status, LM & NTLM is been refused, as it should be.
How to solve it?
Method #1 – Through UI,
- Go to Start menu button and open “SecPool.msc”
- Find key “Network Security: Lan Manager authentication”.
- Change the value to “Send LM & NTLM – use NTLM v2 session security if negotiated”. Therefore the best approach is eliminate servers that require LM or NTLM, you can compromise by changing the client policy to allow LM & NTLM, but use NLTM v2 if available, this will at least prevent you from downgrading security on your servers running more recent Windows operating systems.
Method #2 – Using Registry Editor,
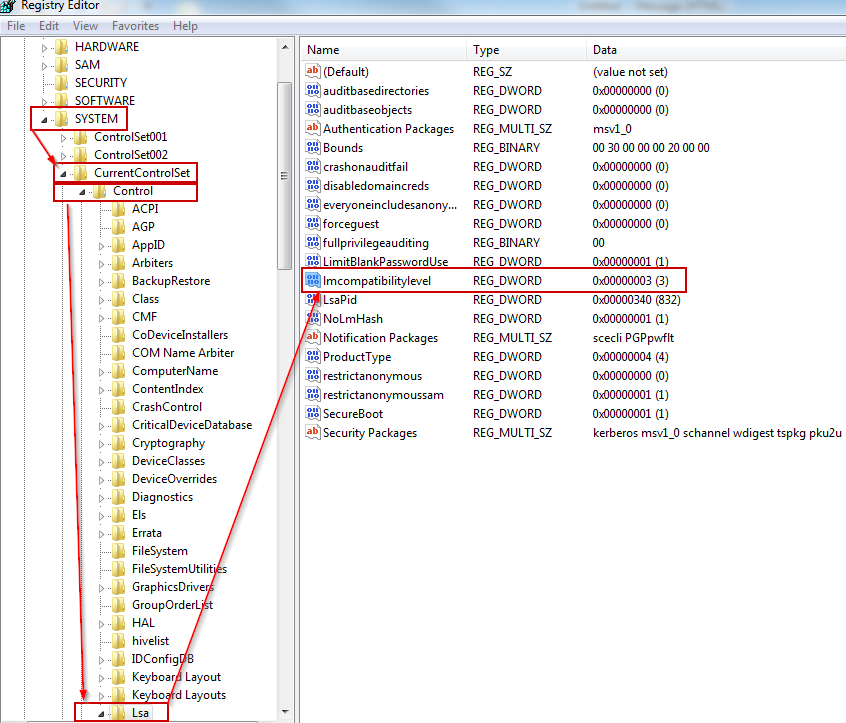
- Go to Start menu button and open “regedit.exe”.
- Find the path “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control”.
- If it doesn’t already exist, create a DWORD value named LMCompatibility.
- Verify the value of the DWORD and save the information in a safe place.
- If the value is set to 2 it’s that means that you’re using use NTLMv1 authentication. Probably the server you’re trying to connect does not accept that kind of authentication. Please set value to 3 to start to use NTLMv2 authentication.
- Save and close all windows.
- Start Remote Desktop client (“mstsc.exe”) and try again to connect.
- Verify if that works fine.
Source information:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc960646.aspx
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/2006.08.securitywatch.aspx
Hope you find it useful.
RMC